Design thinking is a human-centered approach to innovation that will alter the way you develop products, services, processes, and organizations. It is based on understanding customer demands, quick prototyping, and brainstorming to come up with creative ideas.
The design thinking framework encourages designers to think creatively and develop strategies that lead to the creation of user-friendly products that solve a specific problem. It’s vital to notice that it is a non-linear and iterative process.
Instead of relying solely on historical data or making risky bets based on instinct rather than evidence, design thinking allows you to make decisions based on what customers actually want.
One reason for the widespread use of design thinking in industries is that it can be used to dismantle problems in any complex system, whether it’s a business, a government, or a social organization. It can be used to explore significant issues, including how to respond to technological and globalization advancement, how to deal with rapid change, and how to support individuals while catering to larger organizations.

It’s crucial to develop and refine skills in User Experience (UX) design in order to understand and respond to quick changes in users’ environments and behavior. In the twenty-first century, many organizations from a variety of industries find design thinking to be a beneficial way for solving problems for their customers.
If you pursue design thinking, you can work as a Product Manager, Innovation Manager, Brand Manager, or Design Research Manager in a company. Design thinking emerged as a method for developing sleek technology and commodities. However, this methodology is now widely employed in both the commercial and public sectors, for both business and personal initiatives all over the world, and so has a lot of future scope.
Design Thinking gives you an opportunity to pursue interdisciplinary professions. Some emerging careers in Design Thinking are –
- Designers who can also code have a great set of tools and skills that can help them find relatively new and creative opportunities. There are lots of roles available for people with the capacity to come up with new ideas and launch them swiftly into the market.
- Entrepreneurship and design thinking together have incredible scope. Designers are being included in the inner circles of venture capital firms. More importantly, many of the fastest-growing businesses are thriving as a result of their innovative product or service. By pursuing Design Thinking, you have the potential to be a design entrepreneur.
- Understanding how to use technology to discover how people and groups genuinely think and act is an essential aspect of innovation. Being a hybrid design researcher could be a fantastic job for you if you enjoy working with people and crunching numbers.
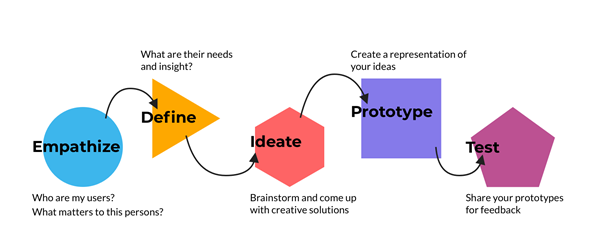
Design thinking involves five stages, namely Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype, Test.
- Empathy- Designers sit down with real people at this stage in the design thinking process and absorb their point of view, way of thinking, and introspection without bias.
- Define- After empathizing, a designer applies what they’ve learned from their research to the human-centric problem at hand, formulating the problem statement. In this stage of the process, designers must articulate the challenge or problem they must solve with their design.
- Ideation- Ideation is the process of coming up with new ideas, which can be performed via a range of strategies such as brainstorming Ideation, when done correctly, helps founders and executives in determining the right problem to tackle and how to do it.
- Prototyping- This is an experimental or trial stage. The goal is to find the ideal solution for each problem encountered. Prototyping usually entails the creation of low-cost, small-scale versions of the product. Specific features can be included to target specific problem-solving scenarios and create the environment for decision-making discussions about what works and what doesn’t.
- Test- Testing is an iterative process. During the testing stage, designers can expect a number of revisions, adjustments, and refinements. As a result, designers can go back to earlier phases to make more iterations, changes, and refinements – or to rule out alternate ideas.
Conclusion-
Design thinking is a concept that can be used in a variety of fields. From human resource management, business management, education, law, and medicine to ICT, and design itself, design thinking principles enable and empower professionals to approach a problem statement step-by-step and consider all essential factors in order to arrive at the ideal solution.
FAQs
- What makes Design Thinking a unique career with great opportunities?
Design Thinking is a career based on creative and problem-focused solutions, is open to ambiguity and vulnerability, enhances analytical and imaginative thinking, includes iterative and agile processes, and is dependent on collaboration and a growth mindset.
- How does the approach of Design Thinking benefit consumers?
Design thinking inverts the usual innovation technique in the consumer world. Instead of producing a new product or service in isolation and then convincing people to buy it, companies can create products and services based on a deep understanding of what customers desire.
- Is design thinking beneficial for the IT sector?
Design thinking is a suitable fit for IT firms that have already implemented an agile framework or want to become more agile. While it may not be applicable in all scenarios, a design thinking approach strongly complements the agile pattern of rapid prototyping, testing, and refactoring.
